- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录3887 > PIC16F84A-04E/SS (Microchip Technology)IC MCU CMOS 4MHZ 1K FLASH 20SSOP
PIC16F84A
DS35007B-page 22
2001 Microchip Technology Inc.
6.2
Oscillator Configurations
6.2.1
OSCILLATOR TYPES
The PIC16F84A can be operated in four different
oscillator
modes.
The
user
can
program
two
configuration bits (FOSC1 and FOSC0) to select one of
these four modes:
LP
Low Power Crystal
XT
Crystal/Resonator
HS
High Speed Crystal/Resonator
RC
Resistor/Capacitor
6.2.2
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR/CERAMIC
RESONATORS
In XT, LP, or HS modes, a crystal or ceramic resonator
is connected to the OSC1/CLKIN and OSC2/CLKOUT
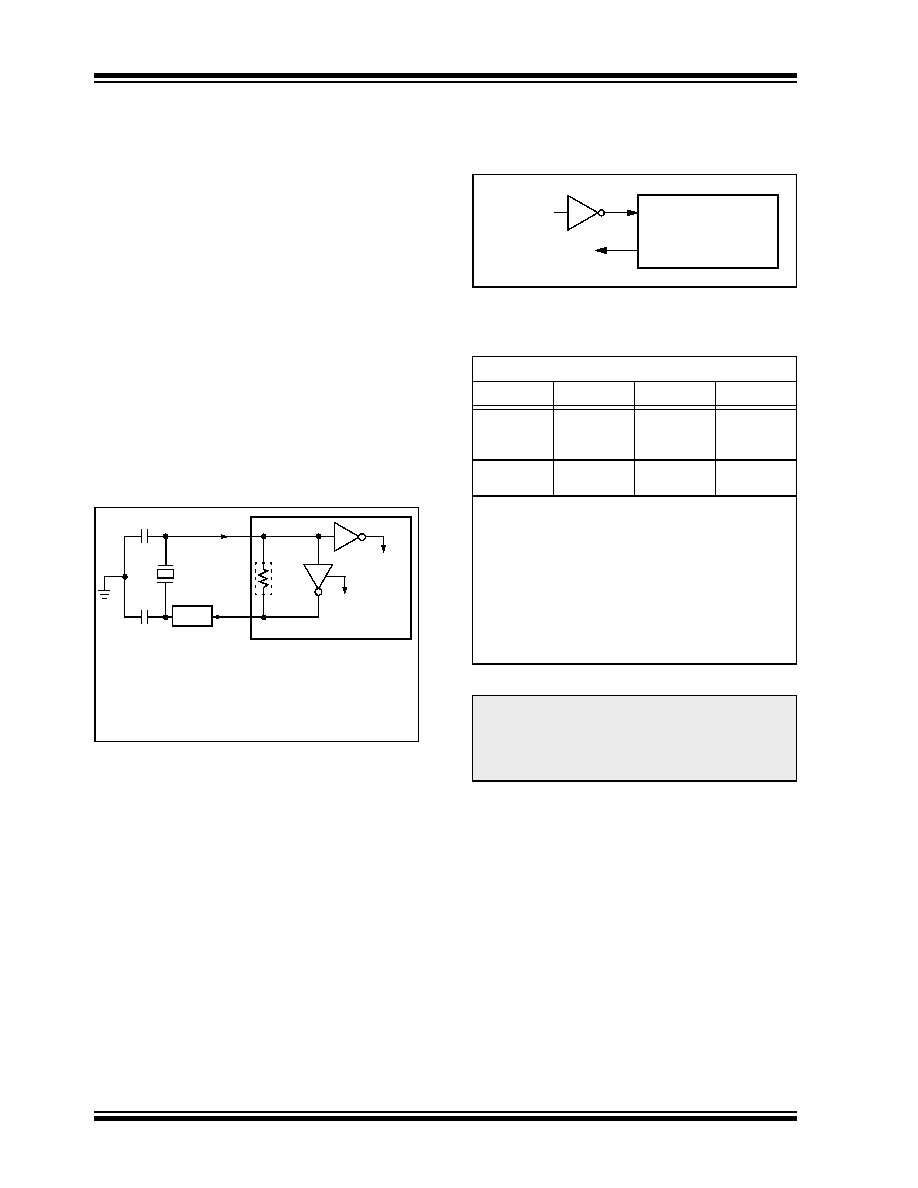
pins to establish oscillation (Figure 6-1).
FIGURE 6-1:
CRYSTAL/CERAMIC
RESONATOR OPERATION
(HS, XT OR LP OSC
CONFIGURATION)
The PIC16F84A oscillator design requires the use of a
parallel cut crystal. Use of a series cut crystal may give
a
frequency
out
of
the
crystal
manufacturers
specifications. When in XT, LP, or HS modes, the
device can have an external clock source to drive the
OSC1/CLKIN pin (Figure 6-2).
FIGURE 6-2:
EXTERNAL CLOCK INPUT
OPERATION (HS, XT OR
LP OSC
CONFIGURATION)
TABLE 6-1:
CAPACITOR SELECTION FOR
CERAMIC RESONATORS
Note 1: See Table 6-1 for recommended values
of C1 and C2.
2: A series resistor (RS) may be required
for AT strip cut crystals.
C1(1)
C2(1)
XTAL
OSC2
OSC1
RF(3)
SLEEP
To
Logic
PIC16FXX
RS(2)
Internal
Ranges Tested:
Mode
Freq
OSC1/C1
OSC2/C2
XT
455 kHz
2.0 MHz
4.0 MHz
47 - 100 pF
15 - 33 pF
47 - 100 pF
15 - 33 pF
HS
8.0 MHz
10.0 MHz
15 - 33 pF
Note:
Recommended values of C1 and C2 are
identical to the ranges tested in this table.
Higher capacitance increases the stability
of the oscillator, but also increases the
start-up time. These values are for design
guidance only. Since each resonator has
its own characteristics, the user should
consult the resonator manufacturer for the
appropriate values of external compo-
nents.
Note:
When using resonators with frequencies
above 3.5 MHz, the use of HS mode rather
than XT mode, is recommended. HS mode
may be used at any VDD for which the
controller is rated.
OSC1
OSC2
Open
Clock from
Ext. System
PIC16FXX
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
PIC16F84A-04E/SO
IC MCU CMOS 4MHZ 1K FLASH 18SOIC
PIC16F785-I/SS
IC PIC MCU FLASH 2KX14 20SSOP
PIC16C433T-I/SO
IC MCU CMOS 8BIT 10MHZ 2K 18SOIC
PIC16C773T-E/SO
IC MCU OTP 4KX14 A/D PWM 28SOIC
PIC16CE623T-30/SO
IC MCU OTP 512X14 EE COMP 18SOIC
PIC16F1825-E/ML
MCU PIC 14K FLASH 1K RAM 16QFN
PIC16F1828-I/SO
IC PIC MCU 8BIT 14KB FLSH 20SOIC
PIC16F688-I/SL
IC PIC MCU FLASH 4KX14 14SOIC
相关代理商/技术参数
PIC16F84A-04I/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 1.75KB 68 RAM 13 I/O 4MHz Ind Temp PDIP18 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F84A-04I/P
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC 8BIT FLASH MCU 16F84 DIP18
PIC16F84A-04I/SO
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 1.75KB 68 RAM 13 I/O 4MHz Ind Temp SOIC18 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F84A-04I/SO
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:8BIT FLASH MCU SMD 16F84 SOIC18
PIC16F84A-04I/SS
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 1.75KB 68 RAM 13 I/O 4MHz IndTemp SSOP20 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F84A-04I/SS
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:8BIT FLASH MCU SMD 16F84 SSOP20
PIC16F84A-20/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 1.75KB 68 RAM 13 I/O 20MHz PDIP18 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC16F84A-20/P
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC 8BIT FLASH MCU 16F84 DIP18